VNC Virtual Network Computing
VNC
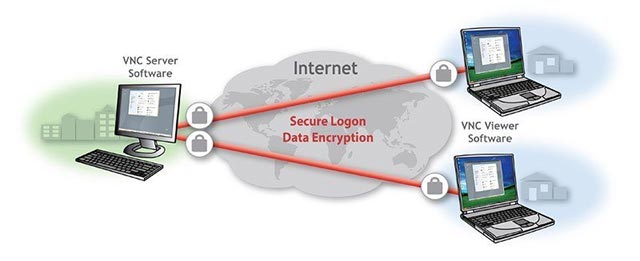
(Virtual Network Computing) provides access to a network device containing graphic applications from another network or over the same network, allowing these applications to be used and managed remotely. A VNC server is installed on a remote device (Operator Panel, PC, Notebook) and a VNC client is installed on the client to be connected (PC, Notebook, Tablet, Mobile Phone). VNC enables the interaction of the installed server and client. The VNC server sends the graphical interface of the device it is working on to the VNC client in the form of an image stream using the RFB (Remote Framebuffer) protocol.
The VNC client processes the data it receives and displays the screenshot on the remote device. Authentication occurs when VNC connects from client to server. When the authentication process is complete, the request for the desktop format and pixel format to be used is notified from the client to the server. As a result of the interaction, the screen view of the device to be connected is provided. Transactions can be made and managed when connected to this device via VNC. At the same time, it provides desktop access by seeing the screen, keyboard and mouse movements.